S.M.A.R.T (Self-Monitoring, Analysis, and Reporting Technology) is a tool designed by IBM for checking the status of hard drives and predicting failures. Here we give a brief overview of performing S.M.A.R.T tests on a Zip recorder. If you are unfamiliar with S.M.A.R.T tests there's a wide range of information readily available online.
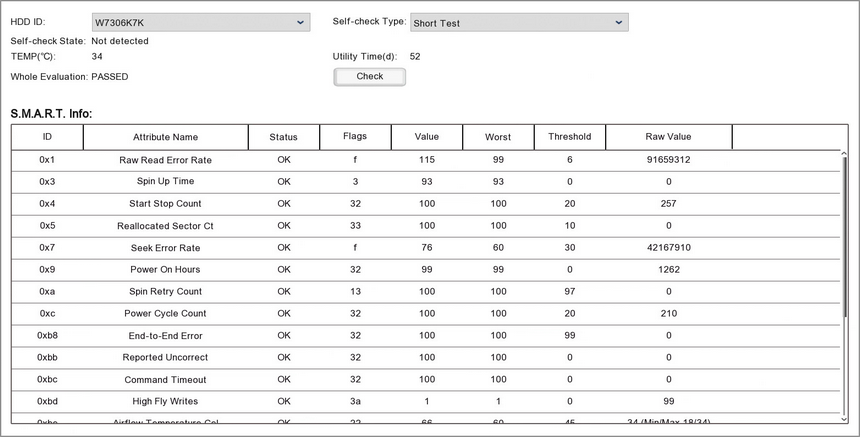
Running a Test
To run a S.M.A.R.T test follow these steps:
1.Select the hard drive you want to test from the HDD ID drop down list.
2.Choose the kind of test you want to perform from the Self-Check Type drop down list.
Short Test - Checks the electrical and mechanical performance scanning parts of the disk. Usually takes a couple of minutes.
Long Test - Thoroughly checks the electrical and mechanical performance scanning the entire disk. This takes several hours.
Conveyance Test - A quick test to check for damage during transport, ideally before the drive has been used for recording.
3.When you have selected the hard drive and test type click the Check button to perform the test.
Reading Test Results
Self-check State
During the test the Self-check State will show the progress of the test as a percent. Once the test has finished it will read "Self test successfully completed".
TEMP(°C)
Gives a live temperature reading for the hard drive.
Utility Time(d)
Shows the total amount of time the hard drive has been powered on in days.
Whole Evaluation
States whether the hard drive has Passed or Failed the test.
S.M.A.R.T Info
This table shows the test result for each attribute of the hard drive.
•ID - The hexadecimal code of the hard drive attribute
•Attribute Name - The part of the hard drive being tested
•Status - Indicates if the hard drive attribute is OK or if it has problem
•Flags - These codes are set by the hard drive manufacturer and give an indication for the reason of the attributes status
•Value - The current health of the attribute
•Worst - The lowest ever value of the attribute in previous tests
•Threshold - The lowest the value can be before it is classed as a fail
•Raw Value - Raw data which is put through an algorithm designed by the manufacturer to give an indication to the attributes overall status